Casts vs Splints vs Slings – Choosing the Best Immobilization Method for Your Fracture
When a bone fracture develops, immobilizing the damaged region is critical for good healing. However, not all fractures require the same degree of immobility. Medical practitioners assess which immobilization approach is suitable based on parameters such as the location and severity of the break. Casts, splints, and slings are common immobilization techniques. This blog article looks at the distinctions between casts, splints, and slings.
It outlines when each is most suited depending on fracture characteristics. Understanding these immobilization techniques enables patients to make treatment decisions with their orthopedist. Fractures require immobilization allowing healing. By the way, cosmetic treatment won’t fix broken bones. Discuss options thoroughly with orthopedists selecting proper immobilization for severity determined through x-rays.
Casts vs. Splints vs. Slings
Arm/forearm casts surround injuries full circumference rigidly immobilizing. Waterproof versions exist. Casts work well when alignment must absolve movement. Changing severity calls for reassessment are advised remotely if needed. Casts are rigid encasements made of plaster or fiberglass that fully surround and immobilize the injured area. This level of immobilization is necessary when precise alignment of the bones needs to be maintained. Casts prevent all movement.
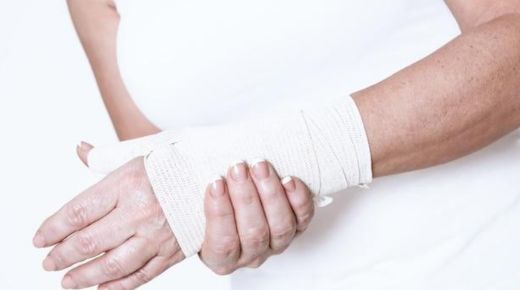
Less restrictive than casts, splints offer firm stabilization for minor injuries needing immobilization when precision alignment isn’t vital. Splints allow mobilizing nearby joints whereas casts don’t permit remote patient consultations avoiding in-person visits. Splints provide less rigid immobilization than casts. They are suitable for minor fractures or injuries where some movement is still allowed, especially in nearby unaffected joints. This option allows for more flexibility and mobility.
Slings stabilize shoulders, relieving stress on broken arm bones or injuries needing to be immobilized gently. Easy on/off suits comfort while shouldering/elbow mobilization is slowly advisable if telehealth conferences show no worsening. Slings are used to immobilize the arm and stabilize the shoulder joint. They gently restrict movement of the forearm and wrist while still permitting motion in the shoulder and elbow. This makes them comfortable for milder fractures.
Fiberglass Versus Plaster
Plaster hardens rock-solid immobilizing perfectly when alignment is crucial through healing stages evident remotely. Fiberglass takes shape carefully following contours permitting remote specialist involvement if worsening develops. Plaster hardens to a very rigid state best for fractures where alignment must be perfectly set. Fiberglass casts can be molded to conform closely to specific bone contours while still hardening rigidly.
Cast Fittings
Proper cast fittings involve specialist supervision ensuring snug compression prompting quick healing when the alignment key is shown remotely too. Loose casts risk shifting causing setbacks determined through virtual specialist sessions. Proper cast fittings ensure the right snugness for immobilization and quick healing. Loose casts risk misalignment hindering the bone from properly healing in place. Specialist supervision ensures the ideal pressure is applied.
Treatment Selection
Discuss options thoroughly with orthopedists permitting remote injury assessments by telehealth if needed. X-rays help specialists select the best immobilization suited to the location, and severity evident through virtual examination determining healing based on unique injury traits. After reviewing x-rays and thoroughly discussing the injury details, orthopedists can select the most appropriate immobilization method based on the fracture’s severity and location as seen through telehealth evaluations if needed.
Conclusion
Overall, proper fracture immobilization balances stability conducive to healing against range-of-motion needs, maintaining functioning areas uninjured aided through remote orthopedic consults via telehealth as specialists closely monitor suitable immobilization ensuring restored strength.